Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
The aberrant methylation of genes that suppress tumorigenesi
2021-03-17
The aberrant methylation of genes that suppress tumorigenesis appears to occur early in tumor development and increase progressively, eventually leading to the malignant phenotype [35]. Genes involved in every step of tumorigenesis can be silenced by this epigenetic mechanism. Hypermethylation of pr
-
br Conclusion In conclusion our findings do not suggest
2021-03-16
Conclusion In conclusion, our findings do not suggest that HT is an important determinant of future AD risk and are in line with a recent Cochrane review stating that HT is not indicated for preventing dementia or cognitive decline in postmenopausal women [13]. Contributors Conflict of inte
-
nefiracetam australia Although several genomic technologies
2021-03-16
Although several genomic technologies, including the generation of ERRγ-specific knockout mice, have revealed that ERRγ plays a pivotal role in cellular bioenergetics [1], its involvement in other metabolic pathways has been appreciated only recently. Therefore, we highlight recent findings on the r
-
The role of Epac in the regulation of intracellular
2021-03-16
The role of Epac in the regulation of intracellular Ca homeostasis and contractility is still matter of debate. In rat adult cardiomyocytes, acute Epac stimulation decreased the amplitude of Ca transients [6], [9], [10] with either no changes [6] or increments [9] in cell shortening, suggesting an e
-
br STAR Methods br Author Contributions br Acknowledgments T
2021-03-16
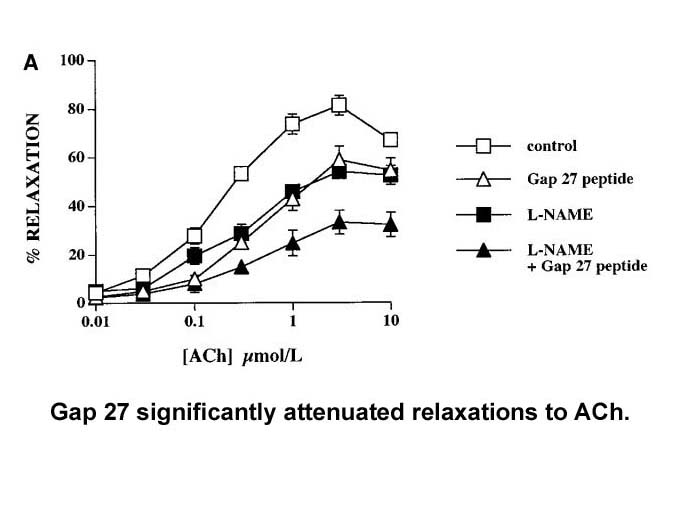
STAR★Methods Author Contributions Acknowledgments The authors thank Monika Kuhn for excellent technical assistance and Dr. Antje Schäfer for valuable scientific input. H.S. was supported by the DFG (FZ 82; Graduate School of Life Sciences and SCHI 425-6/1), and A.V.S. by Northwestern Univer
-
In conclusion we provide convincing evidence that the
2021-03-16
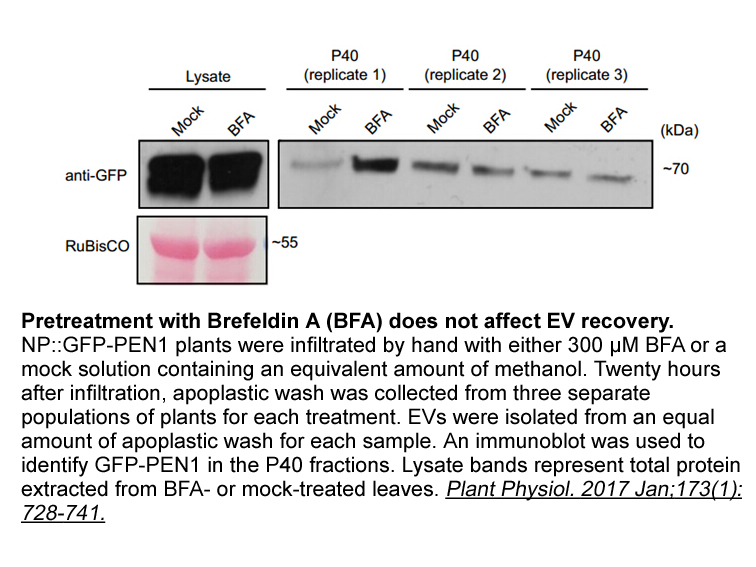
In conclusion, we provide convincing evidence that the PRRSV-induced SGs are indeed bona fide SGs. While we determined that mRNA is present in the PRRSV-induced SGs, we did not distinguish its origin. Future studies will need to determine whether the mRNA stored in PRRSV-induced SGs is of cellular o
-
The pseudo DUBs KIAA and Abraxas are required
2021-03-16
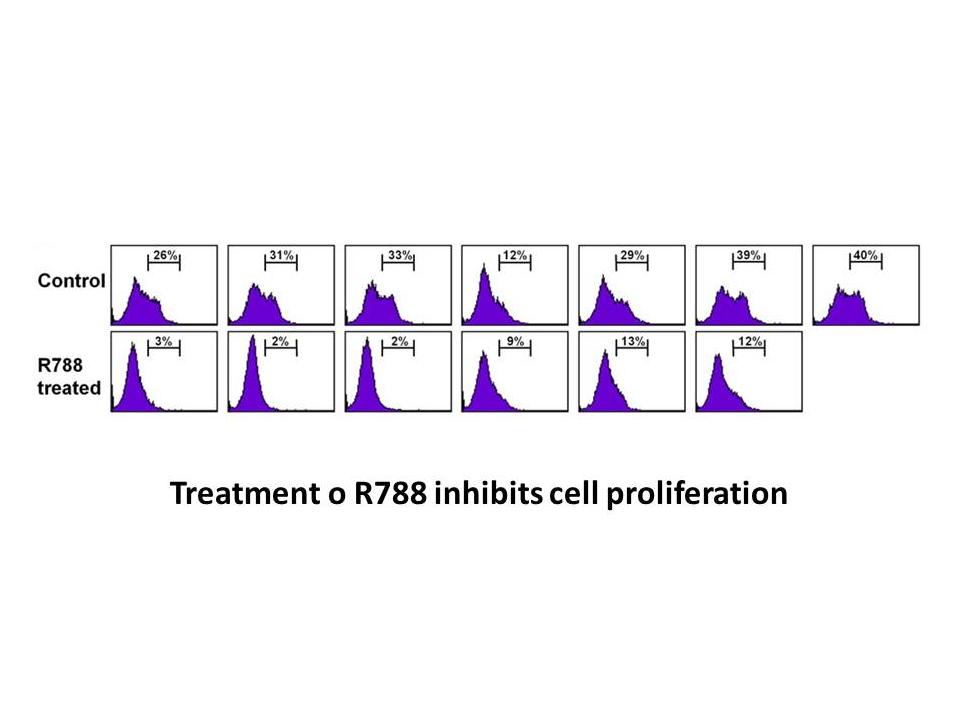
The pseudo DUBs KIAA0157 and Abraxas are required for the catalytic function of BRCC36. Comparison of the BRCC36–KIAA0157 heterodimer structure with an inactive BRCC36 homodimer structure provides a model for understanding how this functional interplay is achieved. As shown in schematic form in Figu
-
Also our data from this study
2021-03-16
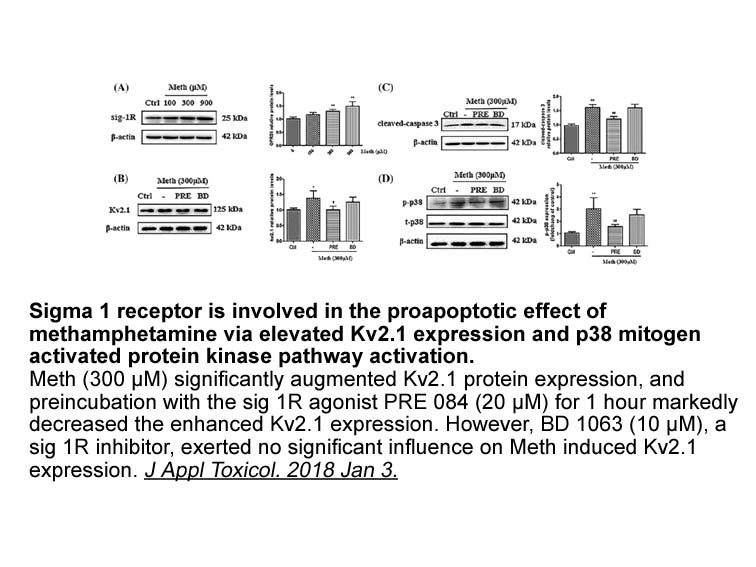
Also, our data from this study indicate that gestational GC exposure altered hematological and hemorheological parameters, however reports exist that altered blood rheological markers are associated with atherosclerosis and CVD (Tzoulaki et al., 2007). Also, the platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) ha
-
Upstream Stimulatory Factor USF binding to the E box
2021-03-16
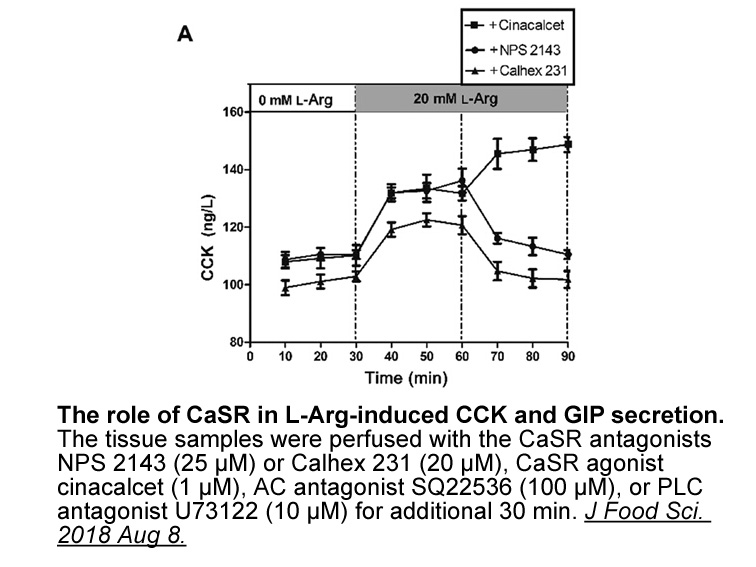
Upstream Stimulatory Factor (USF) binding to the −65 E-box is required for the regulation of FAS promoter activity in fasting/feeding [97], [98]. DNA-PK are identified as a USF-interacting protein [99]. In response to feeding/insulin, the transient double-stranded DNA breaks occurred during the tran
-
br Materials and methods br Results br Discussion
2021-03-16
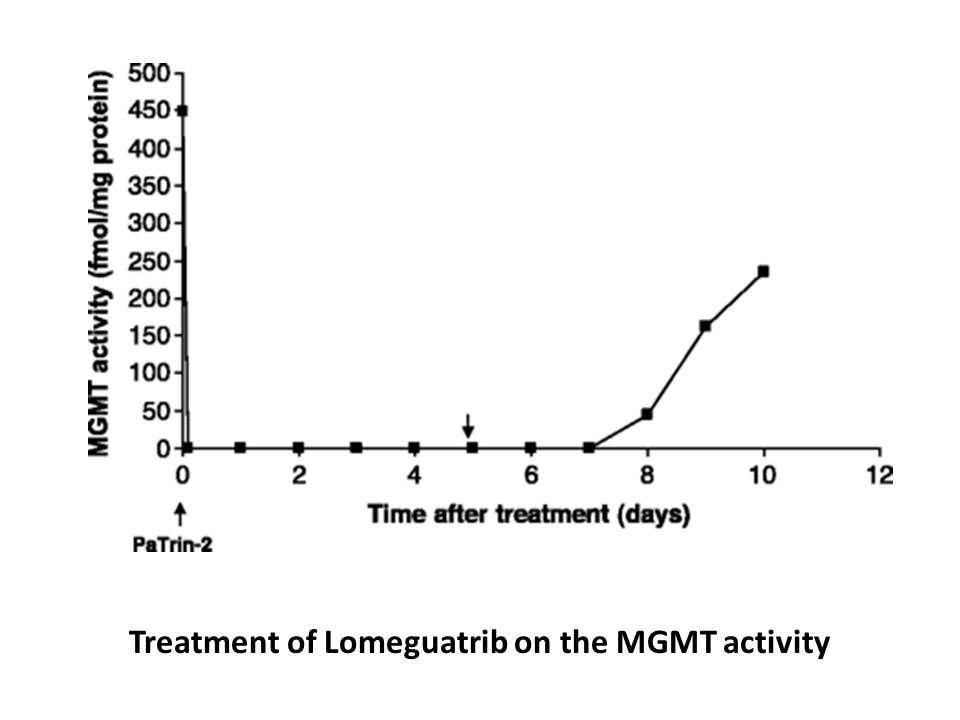
Materials and methods Results Discussion ParI, the first C5-DNA-MTase from a psychrophilic bacterium to be characterized, displays DNA methylation activity in vivo and in vitro. Its biophysical characteristics are consistent with large regions of disorder including thermal unfolding transit
-
Recently we have demonstrated that the synthesis of
2021-03-16
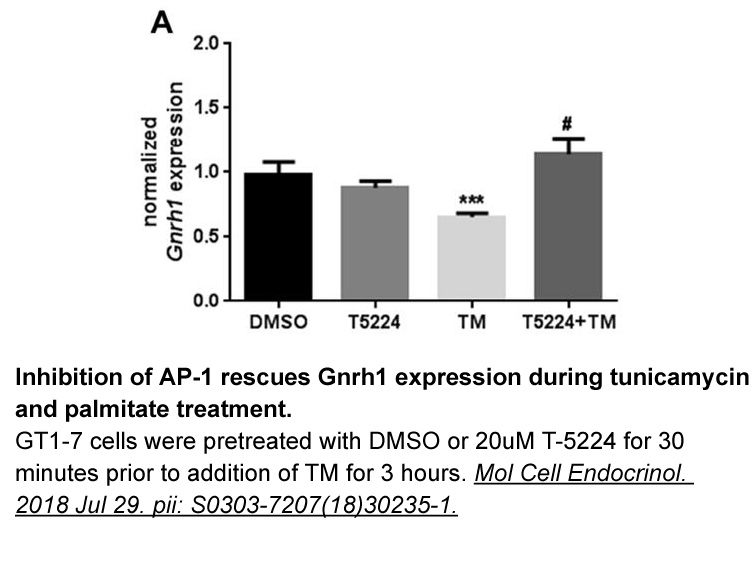
Recently we have demonstrated that the synthesis of cysteinyl-LTs from LTA4 by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) is directly associated with the activation of the CysLT2 receptor (CysLT2R) in a typical autocrine fashion, and that solely the CysLT2R is responsible for the increase in in
-
br Materials and methods br Results and discussion
2021-03-16

Materials and methods Results and discussion Conclusions Conflict of interest Acknowledgments This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31302162, 31171762), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program,
-
A previous report showed that
2021-03-16
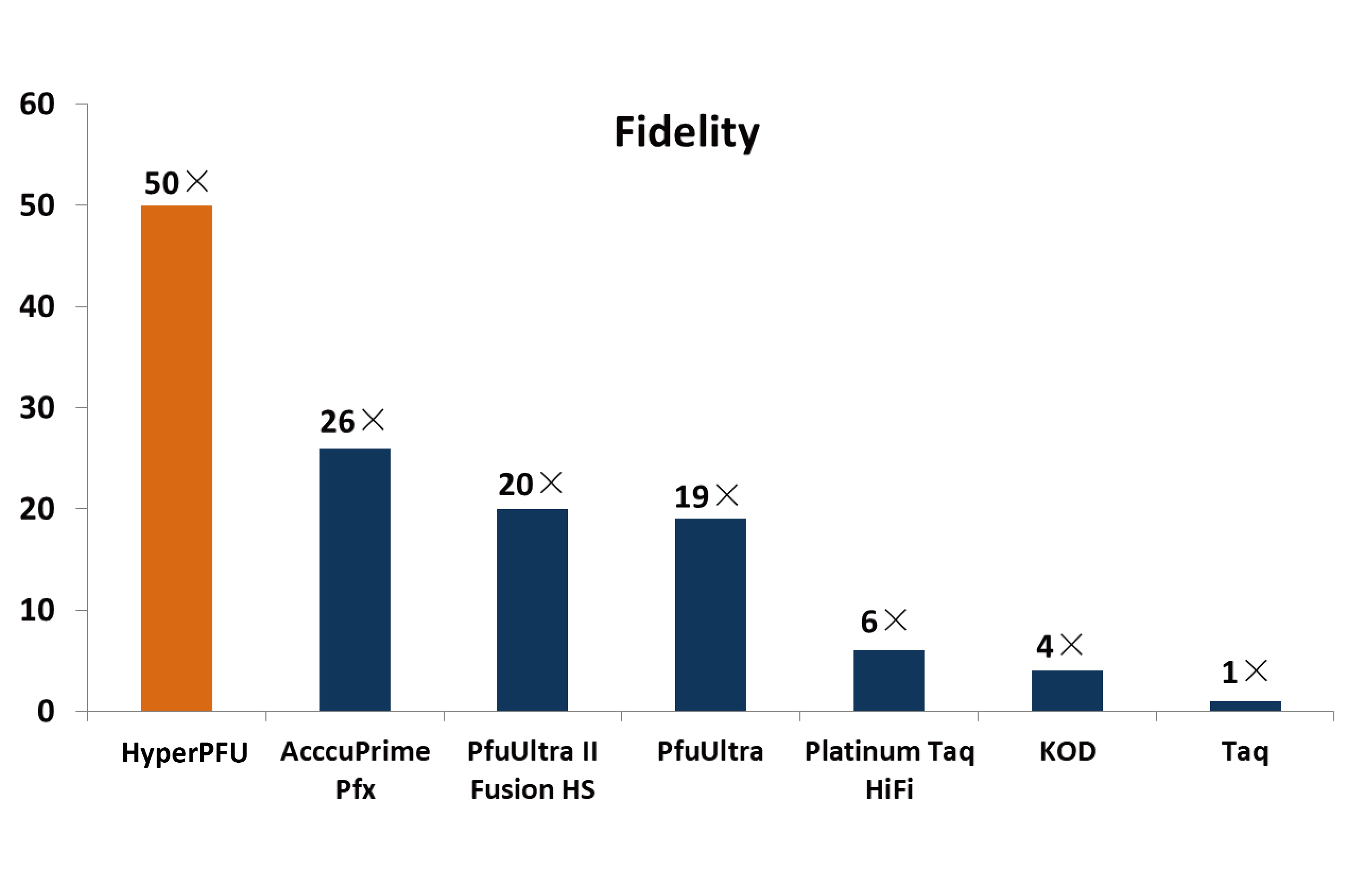
A previous report showed that the transfer of the CSF1 gene into tumor ANA 12 Supplier induced TAM infiltration into syngeneic BALB/c mice. High expressions of CSF-1 and CSF-1R in tumor and stromal cells and a high TAM density are known to be correlated with poor prognoses in many cancer types. CSF
-
br Methods br Results Our study focused
2021-03-15
Methods Results Our study focused on consecutive postural adjustments (CPAs) between IS and BS (the shaded areas on Fig. 2); that is to say, the Rx kinetics that occur after the end of an upper limb movement. It was dedicated to examining the main features of CPAs and the influence of movement
-
br Study design br Results We enrolled
2021-03-15

Study design Results We enrolled 50 subjects awaiting SOT (15 kidney, 14 liver, 1 liver + small bowel, 11 lung, 9 heart) and 50 controls (Table 1) who were similar with respect to median age (subjects 49.1 yrs., controls 48.6 yrs.) gender (64% male subjects and controls), and CMV-seropositivit
10064 records 309/671 page Previous Next First page 上5页 306307308309310 下5页 Last page